Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
天谷 政樹
High Temperature Corrosion of Materials, 15 Pages, 2024/00
被引用回数:0 パーセンタイル:0.02(Metallurgy & Metallurgical Engineering)Zirconium (Zr)-based alloys are widely used as fuel cladding material for light water reactors. Under a loss-of-coolant accident (LOCA) condition, the oxidation of fuel cladding by high-temperature steam induces the degradation of mechanical properties of the cladding and would affect the integrity of fuel rods and/or assemblies, etc., during LOCA. In this study, the distribution of the elements (zirconium, oxygen, tin, iron and chromium) in Zircaloy-4 cladding specimens oxidized in the temperature range of  1350-
1350-  1700 K in steam was analyzed along the radial direction of the specimens by using SEM/EPMA, and the cause of element distribution in the specimens was discussed in consideration of the morphology of precipitates in the specimens and hypothesized phase diagrams related to the elements contained in the specimens. The form of the particles precipitated and the comparison between SEM/EPMA results and hypothesized phase diagrams of Zr-Sn-O system suggested that the liquefaction of tin-rich material and/or Zr-(Fe,Cr) compounds occurred during the oxidation test. The results obtained indicate that Zircaloy-4 cladding tubes would start melting at the melting point of tin-oxide and the eutectic point of Zr-(Fe,Cr)compounds, which is much lower than the melting point of Zr,
1700 K in steam was analyzed along the radial direction of the specimens by using SEM/EPMA, and the cause of element distribution in the specimens was discussed in consideration of the morphology of precipitates in the specimens and hypothesized phase diagrams related to the elements contained in the specimens. The form of the particles precipitated and the comparison between SEM/EPMA results and hypothesized phase diagrams of Zr-Sn-O system suggested that the liquefaction of tin-rich material and/or Zr-(Fe,Cr) compounds occurred during the oxidation test. The results obtained indicate that Zircaloy-4 cladding tubes would start melting at the melting point of tin-oxide and the eutectic point of Zr-(Fe,Cr)compounds, which is much lower than the melting point of Zr,  -Zr(O), or zirconium oxide (ZrO
-Zr(O), or zirconium oxide (ZrO ).
).
Pham, V. H.; 倉田 正輝; Steinbrueck, M.*
Thermo (Internet), 1(2), p.151 - 167, 2021/09
Since the nuclear accident at Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station in 2011, a considerable number of studies have been conducted to develop accident tolerant fuel (ATF) claddings for safety enhancement of light water reactors. Among many potential ATF claddings, silicon carbide is one of the most promising candidates with many superior features suitable for nuclear applications. In spite of many potential benefits of SiC cladding, there are some concerns over the oxidation/corrosion resistance of the cladding, especially at extreme temperatures (up to 2000 C) in severe accidents. However, the study of SiC steam oxidation in conventional test facilities in water vapor atmospheres at temperatures above 1600
C) in severe accidents. However, the study of SiC steam oxidation in conventional test facilities in water vapor atmospheres at temperatures above 1600 C is very challenging. In recent years, several efforts have been made to modify existing or to develop new advanced test facilities to perform material oxidation tests in steam environments typical of severe accident conditions. In this article, the authors outline the features of SiC oxidation/corrosion at high temperatures, as well as the developments of advanced test facilities in their laboratories, and, finally, give some of the current advances in understanding based on recent data obtained from those advanced test facilities.
C is very challenging. In recent years, several efforts have been made to modify existing or to develop new advanced test facilities to perform material oxidation tests in steam environments typical of severe accident conditions. In this article, the authors outline the features of SiC oxidation/corrosion at high temperatures, as well as the developments of advanced test facilities in their laboratories, and, finally, give some of the current advances in understanding based on recent data obtained from those advanced test facilities.
 C studied by laser heating
C studied by laser heatingPham, V. H.; 永江 勇二; 倉田 正輝; Bottomley, D.; 古本 健一郎*
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 529, p.151939_1 - 151939_8, 2020/02
被引用回数:14 パーセンタイル:87.35(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)As expected for accident tolerant fuels, investigation of steam oxidation for silicon carbide under the conditions beyond design basis accident scenarios is needed. Many studies focused on steam oxidation of SiC at temperatures up 1600 C have been conducted and reported in the literature. However, behavior of SiC in steam at temperatures above 1600
C have been conducted and reported in the literature. However, behavior of SiC in steam at temperatures above 1600 C still remains unclear. To complete this task, we have designed and manufactured a laser heating facility for steam oxidation at extreme temperatures. With the facility, we report the first results on the steam oxidation behavior of SiC at temperatures range of 1400-1800
C still remains unclear. To complete this task, we have designed and manufactured a laser heating facility for steam oxidation at extreme temperatures. With the facility, we report the first results on the steam oxidation behavior of SiC at temperatures range of 1400-1800 C for short term exposure of 1-7 h under atmospheric pressure. Based on the mass change of SiC samples, parabolic oxidation rate and linear volatilization rate were calculated. The oxidation layer appears to be maintained at 1800
C for short term exposure of 1-7 h under atmospheric pressure. Based on the mass change of SiC samples, parabolic oxidation rate and linear volatilization rate were calculated. The oxidation layer appears to be maintained at 1800 C in steam, but the bubble formation phenomenon suggests other volatilization reactions may limit its life.
C in steam, but the bubble formation phenomenon suggests other volatilization reactions may limit its life.
Pham, V. H.; 永江 勇二; 倉田 正輝; 古本 健一郎*; 佐藤 寿樹*; 石橋 良*; 山下 真一郎
Proceedings of International Nuclear Fuel Cycle Conference / Light Water Reactor Fuel Performance Conference (Global/Top Fuel 2019) (USB Flash Drive), p.670 - 674, 2019/09
Silicon carbide (SiC) has recently attracted much attention as a potential material for accident tolerant fuel cladding. To investigate the performance of SiC in severe accident conditions, study of steam oxidation at high temperatures is necessary. However, the study focusing on steam oxidation of SiC at temperatures above 1600 C is still certainly limited due to lack of test facilities. With the extreme oxidation/corrosion environment in steam at high temperatures, current refractory materials such as alumina and zirconia would not survive during the tests. Application of laser heating technique could be a great solution for this problem. Using laser heating technique, we can localize the heat and focus them on the test sample only. In this study, we developed a laser heating facility to investigate high-temperature oxidation of SiC in steam at temperature range of 1400-1800
C is still certainly limited due to lack of test facilities. With the extreme oxidation/corrosion environment in steam at high temperatures, current refractory materials such as alumina and zirconia would not survive during the tests. Application of laser heating technique could be a great solution for this problem. Using laser heating technique, we can localize the heat and focus them on the test sample only. In this study, we developed a laser heating facility to investigate high-temperature oxidation of SiC in steam at temperature range of 1400-1800 C for 1-7 h. The oxidation kinetics is then being studied based on the weight gain and observation on cross-sectioned surface of tested sample using field emission scanning electron microscope. Off-gas measurement of hydrogen (H
C for 1-7 h. The oxidation kinetics is then being studied based on the weight gain and observation on cross-sectioned surface of tested sample using field emission scanning electron microscope. Off-gas measurement of hydrogen (H ) and carbon monoxide (CO) generated during the test is also being conducted via a sensor gas chromatography. Current results showed that the SiC sample experienced a mass loss process which obeyed paralinear laws. Parabolic oxidation rate constant and linear volatilization rate constant of the process were calculated from the mass change of the samples. The apparent activation energy of the parabolic oxidation process was calculated to be 85 kJ.mol
) and carbon monoxide (CO) generated during the test is also being conducted via a sensor gas chromatography. Current results showed that the SiC sample experienced a mass loss process which obeyed paralinear laws. Parabolic oxidation rate constant and linear volatilization rate constant of the process were calculated from the mass change of the samples. The apparent activation energy of the parabolic oxidation process was calculated to be 85 kJ.mol . The data of the study also indicated that the mass change of SiC under the investigated conditions reached to its steady stage where hydrogen generation became stable. Above 1800
. The data of the study also indicated that the mass change of SiC under the investigated conditions reached to its steady stage where hydrogen generation became stable. Above 1800 C, a unique bubble formation on sample surface was recorded.
C, a unique bubble formation on sample surface was recorded.
Negyesi, M.; 天谷 政樹
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 54(10), p.1143 - 1155, 2017/10
被引用回数:6 パーセンタイル:50.9(Nuclear Science & Technology)This paper deals with the oxidation behavior of Zry-4 nuclear fuel cladding tubes in mixed steam_air atmospheres at temperatures of 1273 and 1473 K. The main goal is to study the oxidation kinetics of Zry-4 fuel cladding in dependence on the air fraction in steam in the range from 0 up to 100%. The purpose of this study is to provide experimental data suitable for an oxidation correlation applicable for thermomechanical analysis codes of nuclear power reactor under severe accidents. The influence of the air addition in steam on parameters of Zry-4 kinetic equation has been quantified using the results of weight gain measurements. At 1273 K, both pre-transient and post-transient regimes were treated. The results of weight gain measurements showed a strong dependence of the Zry-4 oxidation kinetics on the air fraction in steam, especially at 1473 and at 1273 K in the post-transient regime.
成川 隆文; 天谷 政樹
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 53(1), p.112 - 122, 2016/01
被引用回数:7 パーセンタイル:54.81(Nuclear Science & Technology)In order to investigate the effect of oxidation and crystal phase condition on the ballooning and rupture behaviors of cladding tube under simulated loss-of-coolant-accident (LOCA) conditions, laboratory-scale experiments were performed in which internally pressurized non-irradiated Zircaloy-4 (Zry-4) cladding specimens were heated to burst in steam and argon gas conditions. Values of the maximum circumferential strain were normalized by dividing them by engineering hoop stress at the time of rupture. The dependence of the normalized value on burst temperature and the relationship between the normalized value and the length, width and area of rupture opening were evaluated. The correlation between the normalized value and the burst temperature suggested that the fraction of the  phase in Zry-4 cladding specimens affected the strain in the specimens and the oxidation of specimens suppressed the amount of ballooning of the specimens. The relationship between the normalized value and the length, width and area of rupture opening indicated that the length, width and area of rupture opening depended on the crystal phase condition in Zry-4 cladding specimens irrespective of atmosphere in the case of the heating rate of
phase in Zry-4 cladding specimens affected the strain in the specimens and the oxidation of specimens suppressed the amount of ballooning of the specimens. The relationship between the normalized value and the length, width and area of rupture opening indicated that the length, width and area of rupture opening depended on the crystal phase condition in Zry-4 cladding specimens irrespective of atmosphere in the case of the heating rate of  3 K/s.
3 K/s.
宇田川 豊; 永瀬 文久; 更田 豊志
JAERI-Research 2005-020, 40 Pages, 2005/09
急冷開始温度及び急冷前の冷却速度がLOCA時の被覆管延性低下に及ぼす影響を調べることを目的とし、未照射PWR用17 17型ジルカロイ-4被覆管から切り出した試料を水蒸気中、1373及び1473Kで酸化し、ゆっくりと冷却(徐冷)してから急冷した。試験条件のうち、徐冷の速度を2
17型ジルカロイ-4被覆管から切り出した試料を水蒸気中、1373及び1473Kで酸化し、ゆっくりと冷却(徐冷)してから急冷した。試験条件のうち、徐冷の速度を2 7K/s、急冷開始温度を1073
7K/s、急冷開始温度を1073 1373Kの範囲で変化させて複数の試験を行い、冷却条件の異なる試料を得た。酸化,急冷した試料に対しリング圧縮試験,ミクロ組織観察,ビッカース硬さ試験を実施した。急冷開始温度低下に伴い、金属層中に析出する
1373Kの範囲で変化させて複数の試験を行い、冷却条件の異なる試料を得た。酸化,急冷した試料に対しリング圧縮試験,ミクロ組織観察,ビッカース硬さ試験を実施した。急冷開始温度低下に伴い、金属層中に析出する 相の面積割合が大幅に増加し、被覆管の延性が明確に低下した。徐冷速度の減少に伴い、析出した
相の面積割合が大幅に増加し、被覆管の延性が明確に低下した。徐冷速度の減少に伴い、析出した 相の単位大きさ及び硬さの増大が生じたが、面積割合及び被覆管の延性はほとんど変化しなかった。析出
相の単位大きさ及び硬さの増大が生じたが、面積割合及び被覆管の延性はほとんど変化しなかった。析出 相は周りの金属層より硬く、また酸素濃度が高いことから、その延性は非常に低いと考えられる。したがって、析出
相は周りの金属層より硬く、また酸素濃度が高いことから、その延性は非常に低いと考えられる。したがって、析出 相の面積割合増大が、急冷開始温度低下に伴う延性低下促進の近因である。
相の面積割合増大が、急冷開始温度低下に伴う延性低下促進の近因である。
永瀬 文久; 大友 隆; 上塚 寛
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 40(4), p.213 - 219, 2003/04
被引用回数:69 パーセンタイル:96.6(Nuclear Science & Technology)さまざまな冷却材喪失事故条件に適用できる酸化速度式を評価するため、773 1573Kという広い温度範囲において低スズ・ジルカロイ-4被覆管の等温酸化試験を行った。1273
1573Kという広い温度範囲において低スズ・ジルカロイ-4被覆管の等温酸化試験を行った。1273 1573Kでは調べた時間範囲について、773~1253Kでは900sまでの時間範囲について、酸化は2乗則に従った。一方、1253K以下での長時間酸化は、3乗則でよりよく表されることが明らかになった。重量増加に関し2乗則あるいは3乗則定数を評価し、それらの温度依存性を表すアレニウスタイプの式を求めた。3乗則から2乗則への変化及び酸化速度定数の温度依存性に見られる不連続性は、ZrO
1573Kでは調べた時間範囲について、773~1253Kでは900sまでの時間範囲について、酸化は2乗則に従った。一方、1253K以下での長時間酸化は、3乗則でよりよく表されることが明らかになった。重量増加に関し2乗則あるいは3乗則定数を評価し、それらの温度依存性を表すアレニウスタイプの式を求めた。3乗則から2乗則への変化及び酸化速度定数の温度依存性に見られる不連続性は、ZrO の相変態によるものであることが示された。
の相変態によるものであることが示された。
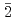 0) face of 4H-SiC
0) face of 4H-SiC吉川 正人; 大島 武; 伊藤 久義; 高橋 邦方*; 北畠 真*
Materials Science Forum, 353-356, p.635 - 638, 2001/00
nタイプ4H-SiC基板の(11-20)及び(1-100)面上に成長させたエピ膜を1100 Cで1時間酸化して、約50nmの酸化膜を作製後、800
Cで1時間酸化して、約50nmの酸化膜を作製後、800 C、850もしくは950
C、850もしくは950 Cで3時間水蒸気中でアニーリングした。その後金蒸着を行って(11
Cで3時間水蒸気中でアニーリングした。その後金蒸着を行って(11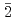 0)及び(1
0)及び(1 00)面上にMOS構造を形成した。CV特性をこれらMOS構造に対して測定し、伝導体近傍の界面準位密度(Dit)並びに界面準位総量(Nit)を求めた。この結果、(11
00)面上にMOS構造を形成した。CV特性をこれらMOS構造に対して測定し、伝導体近傍の界面準位密度(Dit)並びに界面準位総量(Nit)を求めた。この結果、(11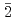 0)面では界面準位総量が水蒸気アニーリングによって減少することがわかった。特に伝導体近傍では、界面準位密度のエネルギー分布が変化し、界面準位密度の低下が認められた。
0)面では界面準位総量が水蒸気アニーリングによって減少することがわかった。特に伝導体近傍では、界面準位密度のエネルギー分布が変化し、界面準位密度の低下が認められた。
 C
C上塚 寛; 大友 隆; 川崎 了
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 23(10), p.928 - 930, 1986/00
被引用回数:5 パーセンタイル:65.85(Nuclear Science & Technology)軽水炉の炉心損傷事故時におけるジルカロイ被覆管の酸化挙動を明らかにするために、微量の水蒸気供給条件(0.1 36mg/cm
36mg/cm ・min)の下でジルカロイ-4の酸化試験を実施した。各試験温度に対して、明らかな供給水蒸気速度の臨界値が認められ、それ以上の供給速度では反応量(酸化重量増)が一定値となった。この結果から水蒸気欠乏(steam starvation)の影響が見られる水蒸気供給速度範囲を各試験温度に対して決定した。その値は1000
・min)の下でジルカロイ-4の酸化試験を実施した。各試験温度に対して、明らかな供給水蒸気速度の臨界値が認められ、それ以上の供給速度では反応量(酸化重量増)が一定値となった。この結果から水蒸気欠乏(steam starvation)の影響が見られる水蒸気供給速度範囲を各試験温度に対して決定した。その値は1000 Cにおける酸化の場合約1.0mg/cm
Cにおける酸化の場合約1.0mg/cm ・min、1400
・min、1400 Cの場合には約4mg/cm
Cの場合には約4mg/cm ・minであった。又、従来のジルカロイ-水蒸気酸化試験における水蒸気供給速度条件より1
・minであった。又、従来のジルカロイ-水蒸気酸化試験における水蒸気供給速度条件より1 2オーダー小さい条件(30mg/cm
2オーダー小さい条件(30mg/cm ・min)で得た試験結果から反応速度定数の温度依存式を決定した。この結果は文献値と極めて良い一致を示した。したがって、本実験で求めた臨界値以上の水蒸気供給速度条件では通常の酸化が生じると結論できる。
・min)で得た試験結果から反応速度定数の温度依存式を決定した。この結果は文献値と極めて良い一致を示した。したがって、本実験で求めた臨界値以上の水蒸気供給速度条件では通常の酸化が生じると結論できる。
上塚 寛; 古田 照夫; 川崎 了
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 20(11), p.941 - 950, 1983/00
被引用回数:35 パーセンタイル:93.84(Nuclear Science & Technology)軽水炉の冷却材喪失条件下でのジルカロイ-4被覆の耐破断特性を調べるために、アルミナペレット内蔵・He加圧の模擬燃料棒を用いて燃料棒破裂-酸化-急冷実験を行なった。燃料棒を水蒸気中で破裂させ、920~1330 Cの各温度で3~180分の等温酸化を行なった後、拘束条件または非拘束条件の下で装置下部からの注水によって急冷した。非拘束条件下の急冷による被覆の破損限界酸化条件は、等温酸化温度1050~1330
Cの各温度で3~180分の等温酸化を行なった後、拘束条件または非拘束条件の下で装置下部からの注水によって急冷した。非拘束条件下の急冷による被覆の破損限界酸化条件は、等温酸化温度1050~1330 Cに対して、等価被覆酸化量(ECR)換算で35~38%であった。970~1050
Cに対して、等価被覆酸化量(ECR)換算で35~38%であった。970~1050 Cに対する限界条件はより高温でのECR値よりやや低かった。一方、拘束条件下の急冷による限界条件は、酸化温度930~1310
Cに対する限界条件はより高温でのECR値よりやや低かった。一方、拘束条件下の急冷による限界条件は、酸化温度930~1310 Cに対して、19~24%ECRであった。この値は安全評価指針における基準値(15%ECR)より十分大きい。又、拘束条件下の急冷による燃料棒の破断挙動に関しては、酸素だけではなく、ジルカロイ-4被覆中に吸収された水素も支配的な役割を果すことがわかった。
Cに対して、19~24%ECRであった。この値は安全評価指針における基準値(15%ECR)より十分大きい。又、拘束条件下の急冷による燃料棒の破断挙動に関しては、酸素だけではなく、ジルカロイ-4被覆中に吸収された水素も支配的な役割を果すことがわかった。
本橋 治彦; 古田 照夫
JAERI-M 82-005, 14 Pages, 1982/03
軽水炉用燃料被覆管ジルカロイ-4を1000 Cおよび1050
Cおよび1050 Cで水蒸気-水素混合ガス気流中で酸化させ、表面に生成された酸化膜の特性について、X線回折法によって調べた。試料表面には混合ガスの組成によって、2種類の酸化膜、即ち単斜晶ZrO
Cで水蒸気-水素混合ガス気流中で酸化させ、表面に生成された酸化膜の特性について、X線回折法によって調べた。試料表面には混合ガスの組成によって、2種類の酸化膜、即ち単斜晶ZrO から成る単層および単斜晶・正方晶ZrO
から成る単層および単斜晶・正方晶ZrO とZrOからなる多層の酸化膜が生成される。単層の酸化膜が形成される場合の酸化速度は、放物線則に従っているが、多層酸化膜の場合は、酸化の初期において直線則に従っている。また多層酸化膜が形成される時、ジルカロイ中には多量の水素が吸収されている。多層酸化膜は、表面付近で単斜ZrO
とZrOからなる多層の酸化膜が生成される。単層の酸化膜が形成される場合の酸化速度は、放物線則に従っているが、多層酸化膜の場合は、酸化の初期において直線則に従っている。また多層酸化膜が形成される時、ジルカロイ中には多量の水素が吸収されている。多層酸化膜は、表面付近で単斜ZrO 、中間層では単斜晶と正方晶ZrO
、中間層では単斜晶と正方晶ZrO がそして酸化膜と金属との界面ではZrOによって構成されている。正方晶ZrO
がそして酸化膜と金属との界面ではZrOによって構成されている。正方晶ZrO は酸化時間の増加と共に単斜晶ZrO
は酸化時間の増加と共に単斜晶ZrO へと変化していることも認められた。
へと変化していることも認められた。
上塚 寛; 古田 照夫; 川崎 了
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 19(2), p.158 - 165, 1982/00
被引用回数:22 パーセンタイル:87.4(Nuclear Science & Technology)軽水炉の冷却材喪失事故時に生ずると予想される内面酸化によるジルカロイ被覆管の脆化挙動を明らかにするために、破裂被覆管内部の雰囲気状態を模擬した滞留水蒸気雰囲気中においてリング状ジルカロイ-4試片を890~1194 Cの温度範囲で等温酸化した。その結果、滞留水蒸気雰囲気中で酸化したジルカロイ-4の脆化は主に吸収水素量に影響されることが明らかになった。100
Cの温度範囲で等温酸化した。その結果、滞留水蒸気雰囲気中で酸化したジルカロイ-4の脆化は主に吸収水素量に影響されることが明らかになった。100 Cにおけるリング圧縮試験で、約500wt.ppm以上の水素を吸収したジルカロイ試片は脆性を示した。本実験の結果は、著しい脆化の原因となる破裂被覆内面における水素吸収が破裂被覆内部の雰囲気状態と強く関係しているという前報で報告した考え方を指示するものである。
Cにおけるリング圧縮試験で、約500wt.ppm以上の水素を吸収したジルカロイ試片は脆性を示した。本実験の結果は、著しい脆化の原因となる破裂被覆内面における水素吸収が破裂被覆内部の雰囲気状態と強く関係しているという前報で報告した考え方を指示するものである。
 -水蒸気反応および急冷の影響
-水蒸気反応および急冷の影響上塚 寛; 古田 照夫; 川崎 了
JAERI-M 9681, 19 Pages, 1981/09
軽水炉のLOCA時に燃料棒が破裂した場合に生じる内面酸化によるジルカロイ被覆脆化におよぼすUO -水蒸気反応および急冷の影響を調べるために、UO
-水蒸気反応および急冷の影響を調べるために、UO ペレット内蔵模擬燃料棒を用いて内面酸化実験を行った。模擬燃料棒を流速1.6g/cm
ペレット内蔵模擬燃料棒を用いて内面酸化実験を行った。模擬燃料棒を流速1.6g/cm ・minの水蒸気流中で破裂させ、900
・minの水蒸気流中で破裂させ、900 1150
1150 Cの各温度で4分間等温酸化した。酸化後のジルカロイ被覆脆化挙動は100
Cの各温度で4分間等温酸化した。酸化後のジルカロイ被覆脆化挙動は100 Cでのリング圧縮試験で調べた。その結果、内面酸化したジルカロイ被覆の脆化は主に吸収水素量に影響されることがわかった。吸収水素量の分析値は最大で2050wt.Ppmであり、Al
Cでのリング圧縮試験で調べた。その結果、内面酸化したジルカロイ被覆の脆化は主に吸収水素量に影響されることがわかった。吸収水素量の分析値は最大で2050wt.Ppmであり、Al O
O ペレット内蔵模擬燃料棒を用いた実験結果と定量的にほぼ一致した。また、UO
ペレット内蔵模擬燃料棒を用いた実験結果と定量的にほぼ一致した。また、UO -水蒸気反応による付加的な脆化は認められなかった。したがって、LOCA条件下の破裂燃料棒内におけるUO
-水蒸気反応による付加的な脆化は認められなかった。したがって、LOCA条件下の破裂燃料棒内におけるUO -水蒸気反応はほとんど生じないと考えられる。酸化後空冷したジルカロイ被覆と水中に急冷したジルカロイ被覆の間での脆化挙動の差はほとんど認められなかった。
-水蒸気反応はほとんど生じないと考えられる。酸化後空冷したジルカロイ被覆と水中に急冷したジルカロイ被覆の間での脆化挙動の差はほとんど認められなかった。
古田 照夫; 上塚 寛; 川崎 了; 橋本 政男; 大友 隆
JAERI-M 9475, 22 Pages, 1981/05
破裂した被覆管の内側表面における酸化膜の拡がりは、軽水炉の冷却材喪失事故中のヒートアップ計算にとって非常に重要な項目の一つである。酸化膜の拡がりを調べるため、900-1150 Cにわたる酸化温度、35-240秒の酸化時間、2-1530g/m
Cにわたる酸化温度、35-240秒の酸化時間、2-1530g/m ・sの水蒸気流速そして、約5-26mmの破裂長さなどの条件で模擬燃料棒の破裂・酸化試験を行った。内側表面での酸化膜の拡がりは、酸化温度、時間そして供給される水蒸気量によって影響を受ける。特に、破裂の長さが大きくなると、酸化膜の拡がりは大きくなっていく。破裂部付近での酸化膜厚は他の部分よりも厚く、膜厚の反応速度式によって与えられる値よりも大きい。
・sの水蒸気流速そして、約5-26mmの破裂長さなどの条件で模擬燃料棒の破裂・酸化試験を行った。内側表面での酸化膜の拡がりは、酸化温度、時間そして供給される水蒸気量によって影響を受ける。特に、破裂の長さが大きくなると、酸化膜の拡がりは大きくなっていく。破裂部付近での酸化膜厚は他の部分よりも厚く、膜厚の反応速度式によって与えられる値よりも大きい。
上塚 寛; 古田 照夫; 川崎 了
JAERI-M 9445, 37 Pages, 1981/04
軽水炉のLOCA時に燃料被覆管が破裂した場合に生じる内面酸化による披覆管脆化挙動を明らかにするために、水蒸気流中で模擬燃料棒破裂・酸化実験を行った。その結果、内面酸化した燃料被覆管の脆化は被覆中に吸収された水素による水素脆化であることが明らかになった。100 Cにおけるリング圧縮試験の結果、ジルカロイ被覆管は酸化温度が1000
Cにおけるリング圧縮試験の結果、ジルカロイ被覆管は酸化温度が1000 C以上の場合、吸収水素量200
C以上の場合、吸収水素量200 300w.T.Ppm以上で脆化することがわかった。酸化温度が932
300w.T.Ppm以上で脆化することがわかった。酸化温度が932 972
972 Cの場合には500
Cの場合には500 750w.T.Ppm以上で脆化していた。被覆中に吸収された水素はprior-
750w.T.Ppm以上で脆化していた。被覆中に吸収された水素はprior- 結晶粒界近傍に1
結晶粒界近傍に1 m以下の微細な水素化物として析出していた。破裂開口中心から軸方向に15
m以下の微細な水素化物として析出していた。破裂開口中心から軸方向に15 45mm離れた位置に水素吸収のピークがあった。水素吸収のピーク位置が酸化条件の違いによって変化することから内面酸化に伴う被覆中への水素吸収は内面の雰囲気、特に水素と水蒸気の体積比(V
45mm離れた位置に水素吸収のピークがあった。水素吸収のピーク位置が酸化条件の違いによって変化することから内面酸化に伴う被覆中への水素吸収は内面の雰囲気、特に水素と水蒸気の体積比(V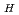
 /V
/V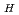

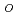 )に影響されると考えられる。
)に影響されると考えられる。
上塚 寛; 古田 照夫; 川崎 了
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 18(9), p.705 - 717, 1981/00
被引用回数:39 パーセンタイル:95.7(Nuclear Science & Technology)軽水炉のLOCA時に燃料被覆管が破裂した場合に生じる内面酸化による被覆管脆化挙動を明らかにするために、水蒸気流中で模擬燃料棒破裂・酸化実験を行なった。 その結果、内面酸化した燃料被覆管の脆化は被覆中に吸収された水素による水素脆化であることが明らかになった。100 Cにおけるリング圧縮試験の結果、ジルカロイ被覆管は酸化温度が1000
Cにおけるリング圧縮試験の結果、ジルカロイ被覆管は酸化温度が1000 C以上の場合、吸収水素量200~300wt.ppm以上で脆化することがわかった。 酸化温度が932~972
C以上の場合、吸収水素量200~300wt.ppm以上で脆化することがわかった。 酸化温度が932~972 Cの場合には500~750wt.ppm以上で脆化することがわかった。 被覆中に吸収された水素はprior-
Cの場合には500~750wt.ppm以上で脆化することがわかった。 被覆中に吸収された水素はprior- 結晶粒界近傍に1
結晶粒界近傍に1 m以下の微細な水素化物として析出していた。 破裂開口中心から軸方向に15~45mm離れた位置に水素吸収のピークがあった。 水素吸収のピーク位置は酸化温度と水蒸気流速の違いによって変化した。
m以下の微細な水素化物として析出していた。 破裂開口中心から軸方向に15~45mm離れた位置に水素吸収のピークがあった。 水素吸収のピーク位置は酸化温度と水蒸気流速の違いによって変化した。
古田 照夫; 本橋 治彦
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 95(3), p.303 - 306, 1980/00
被引用回数:14 パーセンタイル:94.62(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)軽水炉の冷却材喪失事故時に燃料棒が破裂すると、ジルカロイ被覆管は外面だけでなく内面も水蒸気と酸化反応を起こす。この時、内面の酸化膜は外面の稠蜜な被膜と異なった多孔質な被膜となる場合がある。ふたつの酸化膜について生成物の同定をX線回折によって行った。その結果、稠蜜な被膜は単斜晶ジルコニアであるのに対して、多孔質な被膜は単斜晶および正方晶ジルコニアの混合物であることが判った。さらに、多孔質被膜に認められる立方晶の回折線についても同定を行ない、従来あまり明確にされていないZrOであることを確認した。
古田 照夫; 川崎 了
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 17(3), p.243 - 245, 1980/00
被引用回数:5 パーセンタイル:70.2(Nuclear Science & Technology)軽水炉の冷却材喪失事故において、ジルカロイ被覆管は内圧のためふくれ変形を起した後水蒸気によって著しく酸化される。そこで、変形を与えた後の酸化速度について、ジルカロイ板を使って昇温中に引張変形を与えた後高温酸化させて検討を加えた。変形を与えた場合の酸化膜厚は変形を与えない場合のそれに比べて厚くなり、酸化が加速されることを認めた。また、変形温度が低いほど、そして同じ変形温度では大きな歪が与えられた場合に酸化速度が早くなることも認めた。なお、酸化前の変形は酸化反応の初期にだけ加速効果を与えることも明らかにした。
原山 泰雄; 古田 照夫
材料科学, 16(4,5), p.173 - 179, 1979/00
大型電算機を使用して、使用目的に適した合金を設計する法が開発されつつある。本論文は合金設計そのものを論じたものではない。軽水炉被覆管(ジルカロイ)を使用する者から見てジルカロイにどのような性質の改善が望ましいかを考えてみた。通常運転時では、焼きしまりと出力急昇時に影響を与えているクリープ強度と被覆寿命を左右する腐食の問題を取り上げ、今後の被覆材質改良の方向を示唆した。事故時として冷却材喪失事故時の被覆のふるまいを解説し、高温強度と酸化による脆化について被覆材質の改良ではかなりむずかしいことを示した。